By Santa J. Bartholomew M.D. FAAP, FCCM
Spiders, Bees & Ants Emerge with the Summer Weather!
With the onset of warm weather in the United States children and their families head outside, vacation in national parks and beaches, and generally enjoy nature. This, unfortunately, comes with some inherent risks that parents need to be aware of. We begin to share our homes and campers and tents with nature’s other creatures: ticks, spiders, centipedes, millipedes, scorpions, bees, wasps, hornets, fire ants, and the slithering snakes looking to get cool in the heat. Today we will take a walk among these creatures, see what to do when bitten, and when to seek medical attention.
Spiders
Belong to a phylum (group) called Arthropoda which is the largest group in the animal kingdom and includes spiders, mites, ticks, and scorpions. Spiders typically live for 12-14 months. They have a claw-like appendage on their head called a Chelicera that has fangs and can extend from the head and inject venom into their prey. Females are larger than their male counterparts and are almost always responsible for envenomation. Spiders have very poor eyesight and mostly move about by sense of touch. There are 20,000 spider species in the U.S.A. and all are venomous except two. The venom of a spider is more potent than a pit viper but the lack of a concentration of venom and a good injection system makes their bites less efficient still, they can cause serious metabolic damage in the victim. The most common envenomation spiders in the United States are the Brown Recluse and Black Widow. These spiders are typically shy and will retreat from threat but will envenomate when they feel threatened: such as a person moving a wood pile in which they are hiding or cleaning in an attic space. The venom of these spiders is cytotoxic, hemotoxic, and neurotoxic.
- Black Widows
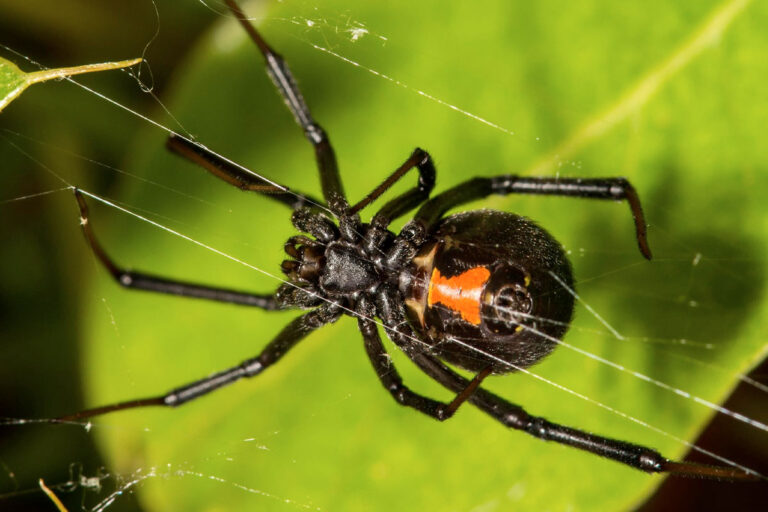
Found throughout North America but is most common in the Southern and Western regions. They are identified by a red coloration on their abdomen and are usually found in woodpiles, under eaves in homes, and where debris accumulates. Also, in outdoor toilets where there are flies in abundance. These spiders typically build webs between objects and humans are bitten when they accidentally disrupt the web. Black widow spiders are responsible for most of the clinically significant envenomations among all species of spiders. Bites from black widows are distinguished from others as they display two puncture marks at the site. Their venom is neurotoxic and causes severe pain at the site of the bite that then spreads to the chest, abdomen, and entire body. Patients typically present within hours of a bite with a history of activities in a garage, attic, camping, or hiking. Within minutes of being bitten, the bite is exquisitely painful, red, and swollen- fang marks may be evident.- Treatment – Initial treatment includes cleaning the wound and tetanus vaccination. Black Widow antivenom is safe and highly effective in most patients relieving symptoms quickly and effectively. Local wound care and debridement may be necessary for wounds not brought to immediate attention.
Black Widow
Black Widow Bite

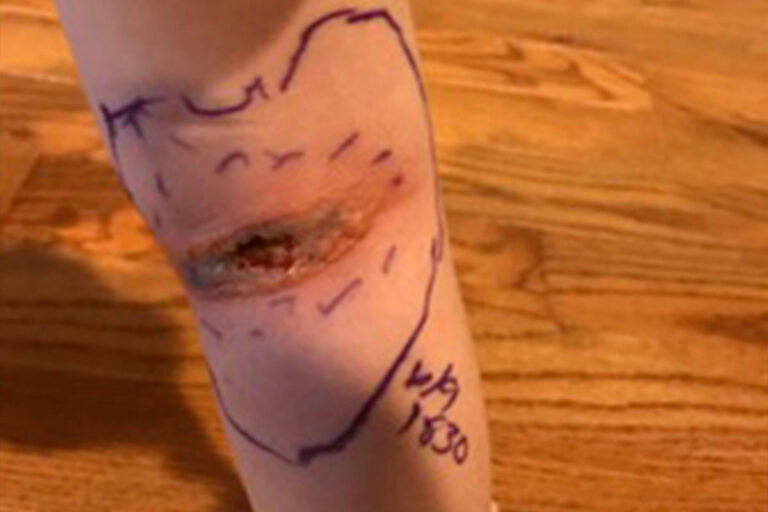
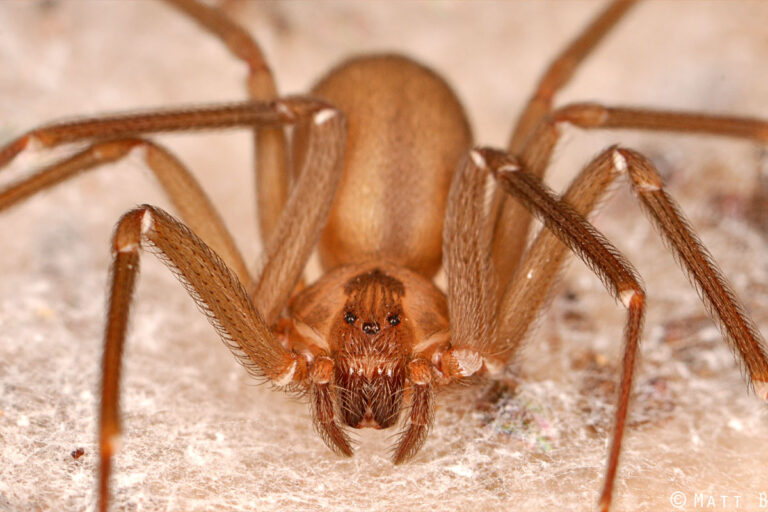
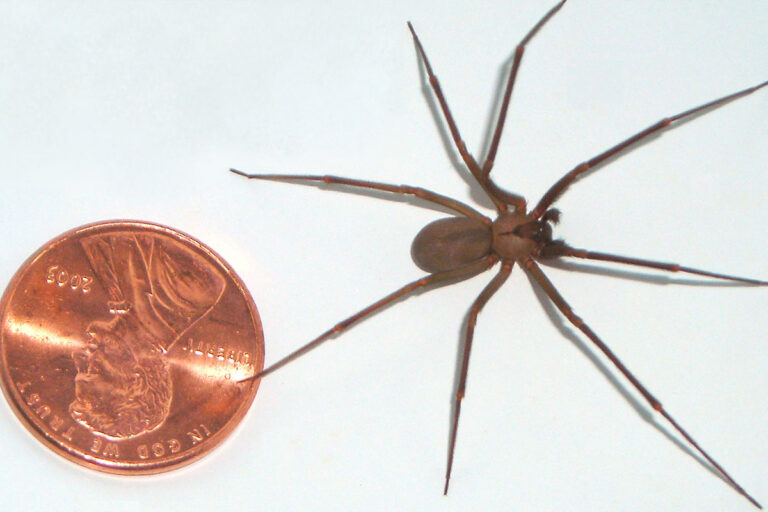
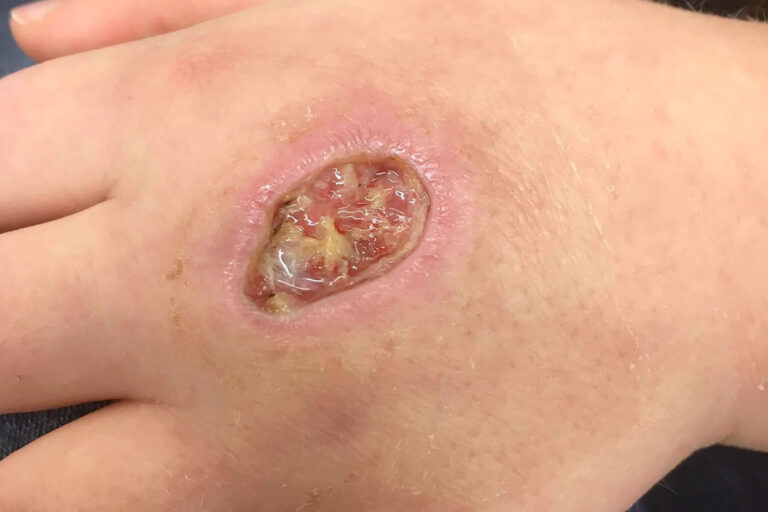
- Brown Recluse (aka Violin Spider) are found mostly in the Midwest and Southern United States. They are usually found in secluded dry sheltered areas like logs, piles of leaves or rocks. If they are indoors, they are typically found in dark closets, shoes, bed corners or attics. Children are more likely to be bitten crawling and cruising in a home or playing in leaves. Most bites occur in the summer months. Brown recluse spiders cannot bite a human without a counter pressure such as a human walking through a web or against the spider directly. The bite produces localized swelling and stinging, and a small white blister develops at the site of the bite. The venom under the skin can quickly destroy the tissue below the skin causing deep wounds. The venom can also set off an inflammatory response that can cause damage to major organs if not treated.
- Treatment
- Clean bite with soap and water
- Apply ice to the area and elevate the limb
- Go to hospital
- In the hospital patient will get tetanus
- Supportive care
- Skin necrosis may need to be debrided
- Treatment
THERE IS NO ANTI-VENOM!
Brown Recluse
Approximate Size
Brown Recluse Bite


Ants
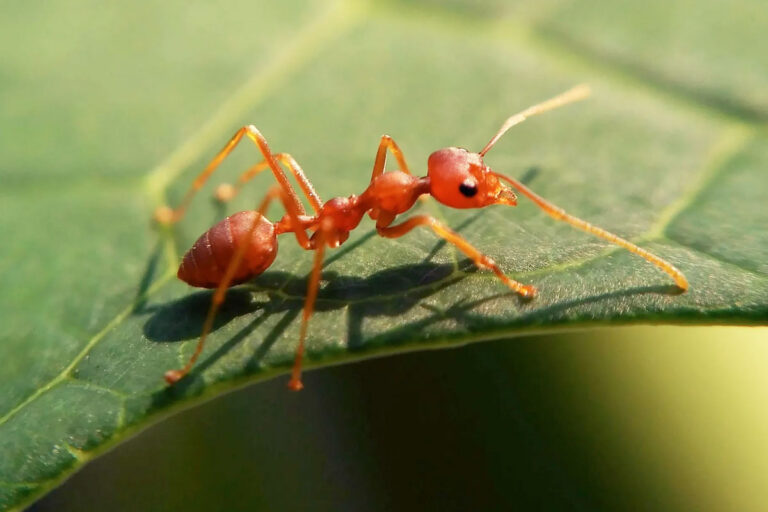
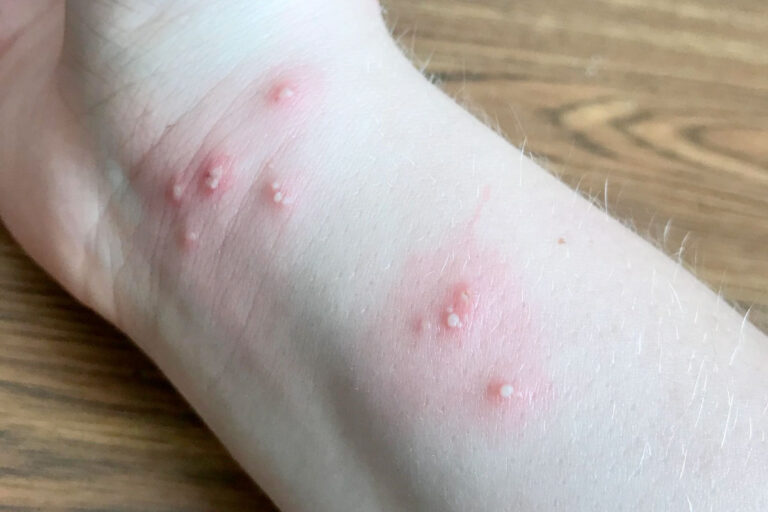
- Fire Ants are aggressive and will sting repeatedly causing very painful lesions. There are two species a red fire ant indigenous to the USA and a black fire ant introduced in Mobile, Alabama 40 years ago. Red fire ants are found predominantly in 14 states in the union: AL, AR, CA, FL, GA, LO, MI, NM, NC, OK, SC, TN, TX, and VA. Black fire ants have been found in AL, northern MS, and southern TN. Fire ants do not need to be provoked to attack and venom in small children can be life-threatening. Typically, bites occur when a nest is disturbed. The ants will swarm and sting any creature they encounter. One ant is capable of multiple stings in very short time frame. Bites occur year-round but are most frequent in summer months. When an ant stings, it grabs onto the victim with its mandible and then arches its body to introduce venom with a stinger on the ant’s abdomen. There is an immediate intense burning and then a redness at the bite site and in a few hours papules appear. These can turn into painful and itchy pustules that can last for days. The venom of these ants can also cause breathing problems, seizures, anaphylaxis, and cardiac collapse.
- Treatment – supportive.
- Other ants for the most part bite but none other than the fire ants in the USA are aggressive. Typically, other ant bites are singular and non-problematic.
Fire Ant
Fire Ant Bites

Centipedes
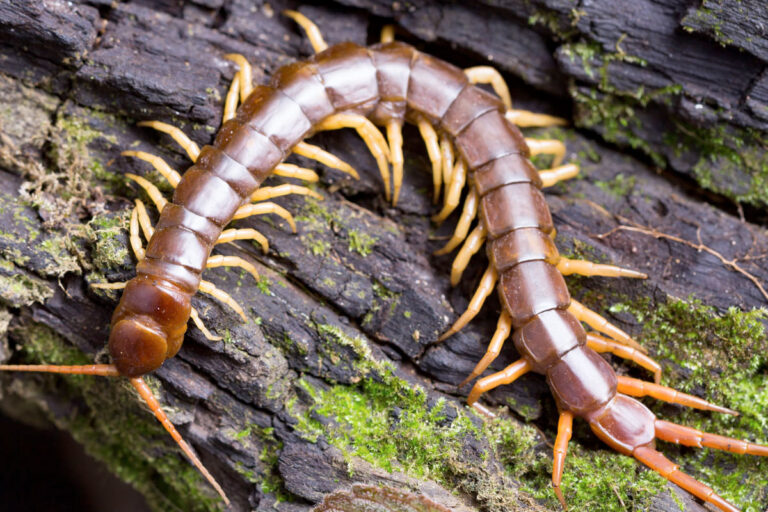
- Centipedes bite and they have venom that is toxic, but bites are relatively uncommon compared to ants and spiders in the United States. There are 3,500 species of centipedes but only 15 have venom that is clinically significant. Centipedes are usually more active at night and in warm climates, so bites are typically more common on summer nights. Bites, although painful are not considered life-threatening. They are found in all 50 states of the USA.
- Treatment – supportive
- Irrigate and wash the site
- Apply ice packs and elevate limbs
- Treatment – supportive
THERE IS NO ANTIDOTE
Centipede
Centipede Bite

Hymenoptera Species
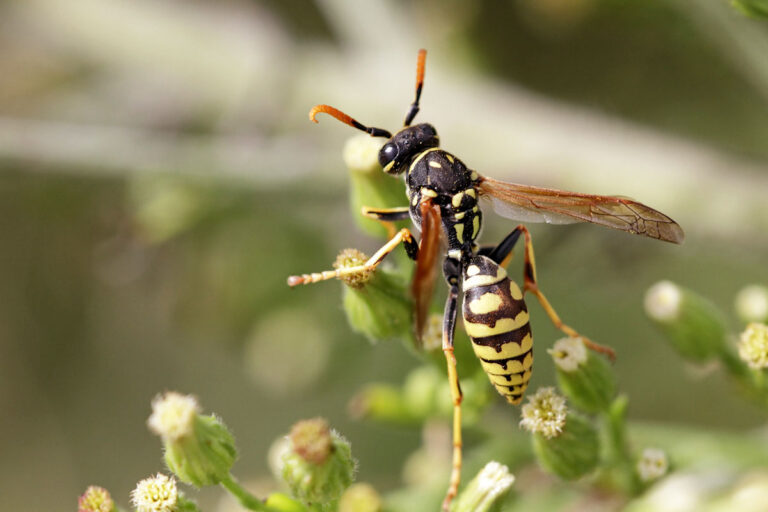
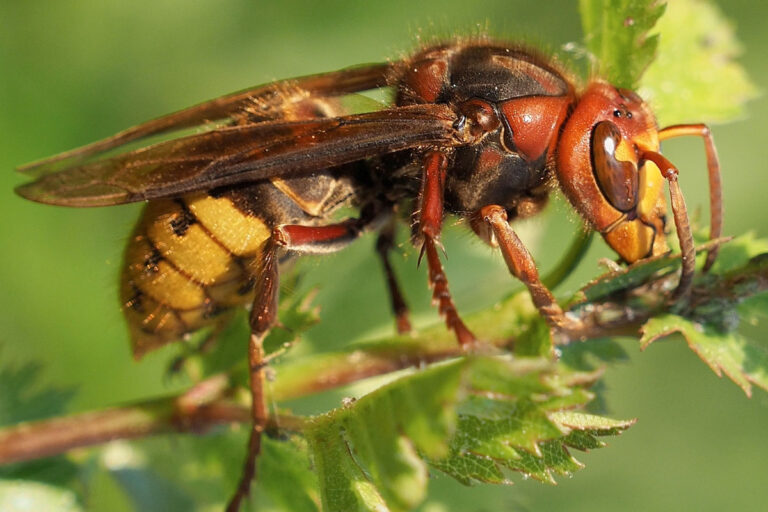
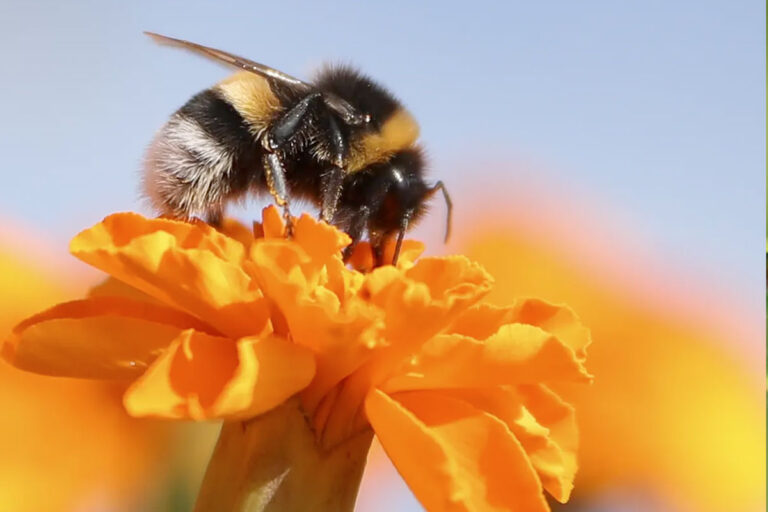
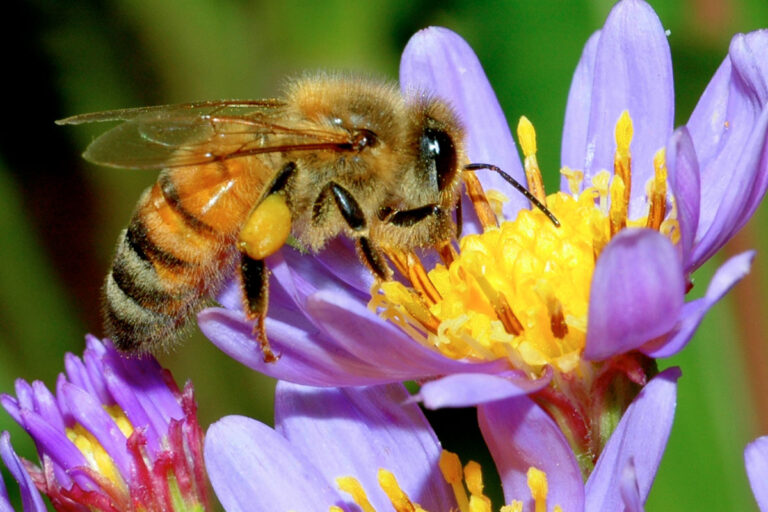
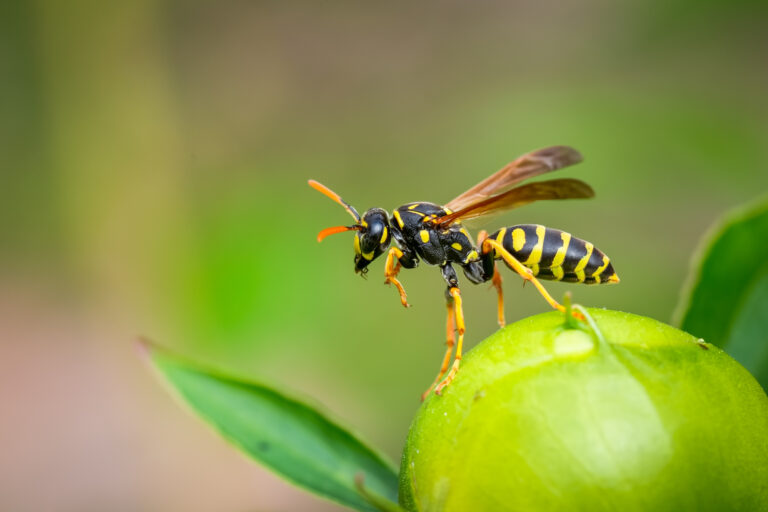
- Bees, Wasps, Yellow Jackets, Hornets + Bumblebees – There are 150,000 species of flying and non-flying insects. Most deaths occur from anaphylaxis and hypersensitivity reactions. The Apidae family of Hymenoptera (Honeybees, Bumblebees) are generally not aggressive and only sting when provoked or threatened. Africanized or Killer bees are very aggressive bees in this family that cause deaths by being able to sting multiple times and often swarm so there are many bees stinging a victim at once. Stings usually occur because of nest disruption.
- Treatment – symptomatic and may include intubation and resuscitation in the case of Killer bee attacks. In some cases prednisone may be helpful, as well as NSAID for pain.
Honey Bee
Wasp


Yellow Jacket
Hornet
Bumblebee







